Essential Woodworking Tools for Beginners
Quality woodworking tools make precise cuts and ensure your woodworking journey begins on solid ground. They lay the foundation for skill development and creative exploration.
Just like with everything else, woodworking tools have also evolved with technological advancements. For instance, the latest tech – laser cutting and engraving – has opened another avenue for wood crafts. With it, creating intricate patterns has become an easy job for beginners.
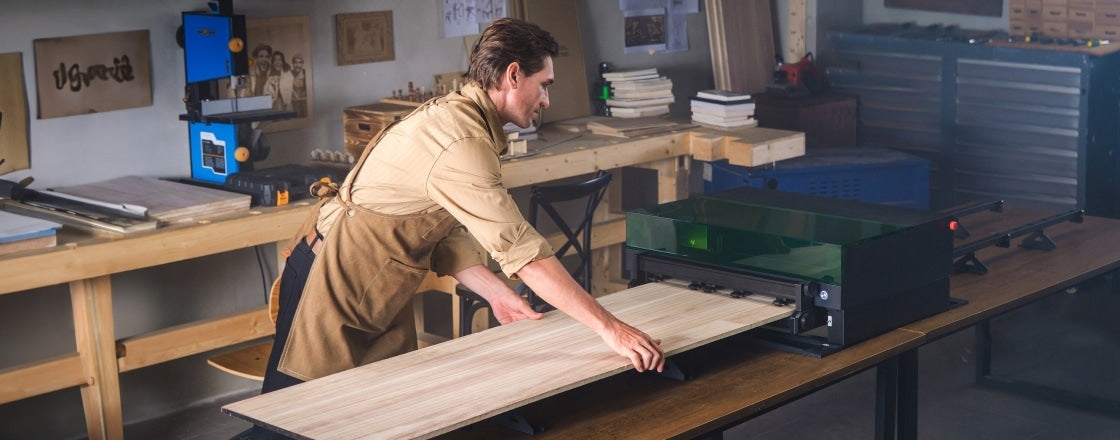

In this article, we explore the essential woodworking tools for beginners. We delve into the use case of each tool, explaining how they fit into various projects.
In This Article
- Classification of Woodworking Tools
- Essential Hand Tools for Woodworking
- Power Tools for Woodworking
- Joinery Tools for Woodworking
- Sanding and Finishing Tools for Woodworking
- Safety Tools for Woodworking
- Storage and Organization Tools for Woodworking
- The Game Changer: Laser Cutting Machines
- More Woodworking Tools
Classification of Woodworking Tools
There are numerous woodworking tools, and it won’t be easy for you to digest if we directly jump into the tools. Classifying them can help you understand the function and find a tool with ease. Considering that, we have placed all tools with the same functionality in one group.
| Group | Tools |
|---|---|
| Measuring & Marking | Measuring Tape, Mechanical Pencil, Centre Punch, Protractor |
| Cutting, Shaping, & Drilling | Handsaws, Chisels, Knives, Power Drills |
| Joinery | Screws, Clamps, Adhesives, Hammer |
| Finishing | Planers, Sanders, Coatings |
| Storage and Organization | Shelves, Magentic Stips, Pegboard |
| Safety Equipment | Leather Apron, Dust Masks, Face Shield |
We also sub-classify these tools based on their operational method: hand-controlled or electrically powered. In the following sections, we will cover all these essential woodworking tools in detail.
Essential Hand Tools for Woodworking
The traditional way is using hand tools. Although it may be time-consuming, the true fun is using these tools. Moreover, for tasks like measuring or marking, hand tools are often the only option you have.
Woodworking Measuring and Marking Tools
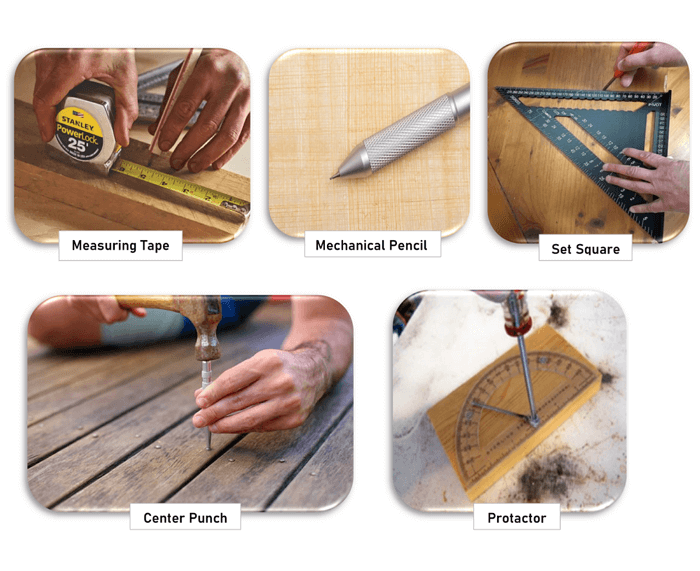

Measuring Tape: It is a compact, retractable tape encased in a plastic or metal body. It extends to measure distances, with a lock to secure the tape’s position. These tapes can be 9 to 35 feet long. For more accuracy and ease of reading, digital versions are also available. They feature an LCD screen for displaying measurements.
Woodworking Squares: Multiple kinds of square tools are used in woodworking. The common ones are:
- Try square: It is a flat, L-shaped tool that has a thick, metal blade and a broad, wooden or plastic handle, used for checking right angles.
- Framing Square: Is L-shaped like a try square. It consists of a calibrated longer and a shorter arm, used for the layout and marking of large-scale projects.
- Speed Square: A thick, triangular tool with a flat right angle and a hypotenuse edge marked with degrees for angle measurements.
Mechanical Pencil/Marking Knife: The mechanical pencil looks like a regular pencil but comes with a clickable mechanism to advance a thin, replaceable lead. It helps in drawing fine consistent thickness lines.
A marking knife also performs a similar job. It has a pointed, slightly beveled blade, to make precise lines. The handle is usually rounded for a comfortable grip.
Centre Punch: It looks like a small, slender rod, with one end tapered to a sharp point and the other end broadened or flattened for striking with a hammer. It is used to create a small dent or a mark in a material to guide the tip of a drill bit. By making an indentation, the center punch ensures the drill bit does not slip and the hole is created at the intended spot.
Angle Guide/Protractor: An angle guide is a tool used for measuring and marking angles. The traditional protractor is usually made of transparent plastic and is semi-circular or circular, with angle measurements marked in degrees along its curved edge.
It helps in precise angle measurement from 0 to 180 degrees or a full 360 degrees, depending on the design. Angle guides come in various forms, including adjustable tools for setting and transferring specific angles onto workpieces.
Woodworking Cutting Tools
Next, we have hand-cutting tools for woodworking.
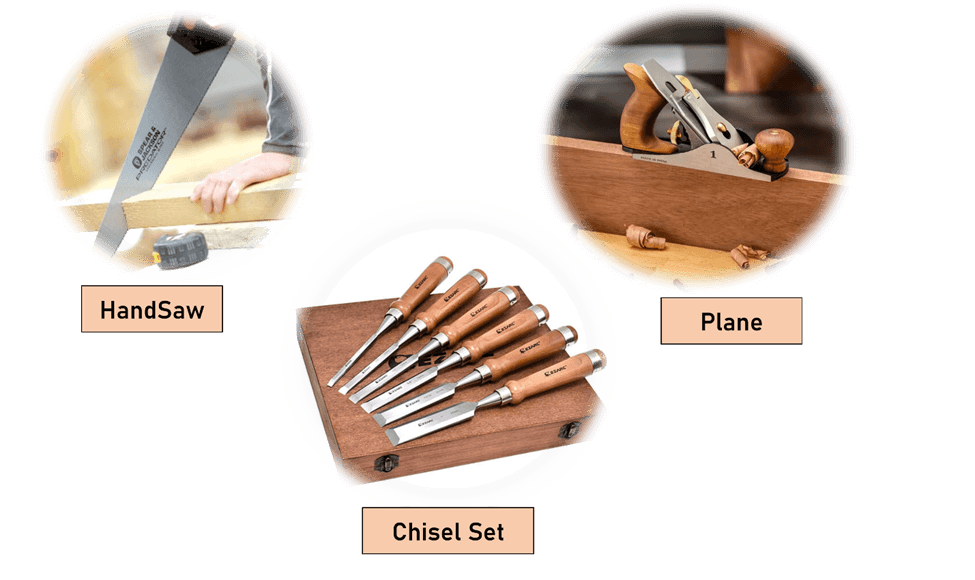
HandSaw: A handsaw consists of a thick blade fixed in a frame, equipped with a wooden or plastic handle. The blade has teeth for cutting, varying in size and spacing depending on the saw type (e.g., rip, cross-cut, or dovetail saw). Hand Saws are used for making precise cuts in wood or shaping wood pieces.
XTOOL LASER
Wood Cutting Made Easy with Laser
With a provided design, laser cutters turn your creativity into reality, no matter how complex the design is.
Learn MoreChisels: A chisel has a long, steel blade with a sharp cutting edge at one end and a handle made of wood at the other. The blade’s width varies for different tasks. Chisels are used for carving or cutting away wood. They are often struck with a mallet to remove material or shape wood joints.
Knives: A woodworking knife features a thin, sharp blade, usually made of hardened steel, fitted with a wooden handle for grip. Craft knives (e.g., utility knives or carving knives) are used for detailed wood cutting, shaping, or whittling.
Planes: A plane consists of a broad, flat base (the body), within which a sharp blade (the iron) is fixed. The tool is pushed across the wood's surface to shave off thin layers, making the surface smooth. Planes are available in multiple sizes and types (e.g., block planes, smoothing planes, or jointer planes) for different stages of woodworking, from rough shaping to fine finishing.
Power Tools for Woodworking
Hand tools may have their charm, but in most instances, the scale of the project demands power tools that quickly and precisely finish the job. This section covers some power and advanced power woodworking tools.
Must-Have Power Woodworking Tools
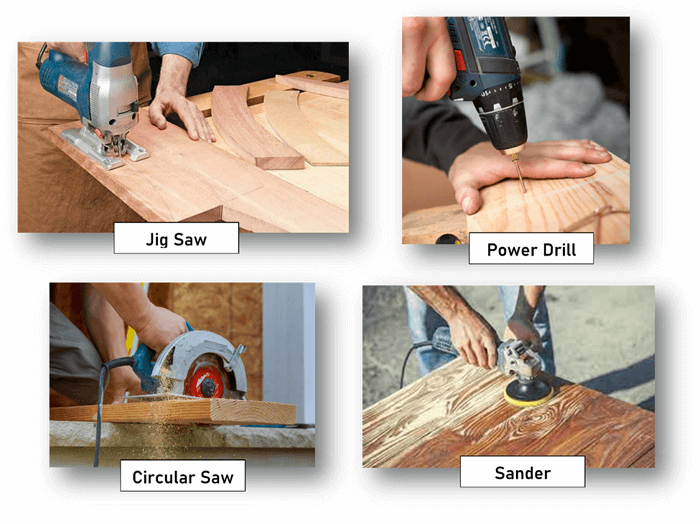
Power Drills: A power drill is used for making holes and driving screws in the wood. It has a cylindrical shape with a grip handle, a trigger to control speed, and a chuck at the end to hold drill bits or screwdriver bits. It is available in both corded and cordless versions.
Circular Saws: This tool has a round, flat blade encased in a protective housing, with teeth along the edge for cutting. It is mounted to a base plate that slides over the material. Circular saws make straight cuts quickly. They are primarily for cutting large sheets of wood like plywood or medium-density fiberboard (MDF).
Jig Saws: A jigsaw is a compact, handheld tool with a narrow, vertical blade that moves up and down. It helps in making intricate cutting patterns, curves, and shapes in wood – perfect for cutting out interior sections without an entry point for the blade.
Sanders: Sanders employs a fast-moving abrasive surface to smooth wood. They have different types, such as orbital, belt, or sheet sanders, each one for a different finishing job. They remove imperfections from the surface to make it ready for painting or varnishing.
Advanced Power Woodworking Tools
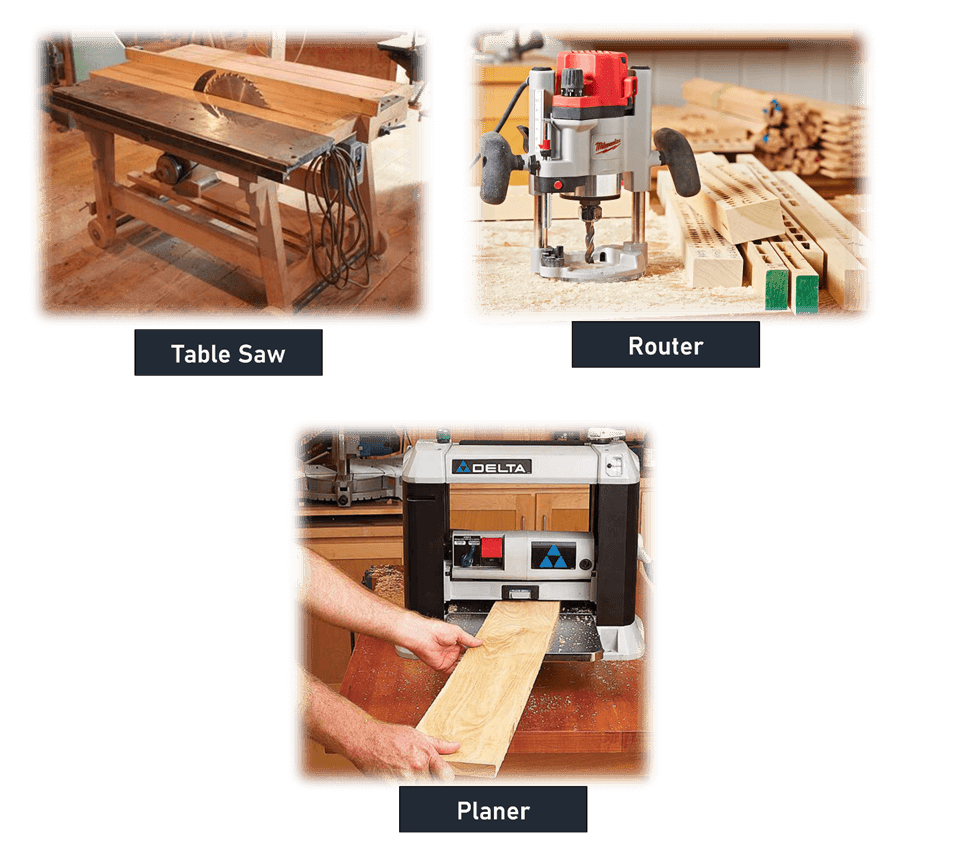
Table Saws: A table saw has a circular blade mounted on an arbor, which protrudes through the surface of a table, providing support for the material being cut. It is equipped with a fence to guide wood for straight cuts and can be adjusted for blade height and angle. They are ideal for ripping large pieces of wood.
Routers: A router is used to hollow out an area in the face of a piece of wood. It consists of a base housing, and a vertically mounted motor with a collet on the end of its shaft to hold router bits.
Routers are highly versatile as they can be fitted with a range of cutting tools. They can perform a variety of tasks including cutting grooves, shaping decorative edges, and creating joints. They are available in stationary (plunge) and handheld (fixed-base) models.
Planers: A planer is used to trim wood to a consistent thickness throughout its length and flat on both surfaces. Flat wood is passed through a rotating cutting head, which proportionally cuts the top layer to maintain singular thickness. Power planers are essential for dimensioning rough lumber, smoothing surfaces, and preparing wood for final finishing.
Joinery Tools for Woodworking
Apart from cutting, shaping, and profiling wood, you also need to join wooden pieces, that’s where these joinery tools come in.
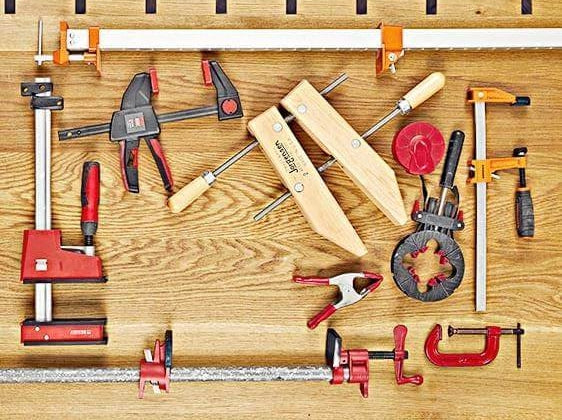

Hammer and Mallet: Hammers have metal heads and are used for driving nails, brads, and other fasteners into wood. Whereas, Mallets are typically made of wood or rubber. They are used to apply controlled force without damaging the wood – best for tapping chisels or adjusting joinery.
Clamps: Clamps hold wood pieces securely together while glue setting or cutting. They come in different types, such as bar clamps, C-clamps, and corner clamps, and cater to different shapes and sizes of workpieces.
Screw-Set and Driver: Steel screws are popular in woodworking for their stronghold. Typically, Philips and Torx are used; the specific one depends upon the project requirements. A screwdriver or power drill with a driver bit is used to drive screws into wood, securing pieces together.
Glues and Adhesives: Wood glue, specifically designed for bonding wood fibers, is essential for strong wood-to-wood bonds. Polyvinyl acetate (PVA) glue is a popular choice due to its strength and ease of use. For tougher jobs and filling, epoxy resin is another excellent option.
Sanding and Finishing Tools for Woodworking
Apart from sanders and planers, these tools are also used for finishing jobs.
Brushes: Brushes help in applying finishes smoothly and evenly. You can choose from a range of sizes and bristle types. Choose including natural, (for oil-based finishes) and synthetic (for water-based finishes).
Paints and Coatings: Paints and coatings protect and enhance the wood's appearance. Options include:
- Stains: Penetrate the wood to accentuate its grain while adding color.
- Varnishes: Provide a durable, protective layer with a gloss finish.
- Polyurethane: Offers a hard, protective finish, available in oil or water-based formulas.
Safety Tools for Woodworking
When working with power tools, there’s always the risk of coming in contact with sharp edges and wooden blisters. So, you need to be very cautious. Wearing these safety tools can help:
Leather Apron: It protects against splinters and minor spills. It covers the front of the body, protecting your clothing. The front pockets can be used for storing small marking tools.
Dust Masks: During sanding or sawing, fine dust particles fill the air. A dust mask is necessary to prevent inhalation of these particles.
Face Shield: When operating power tools that can throw debris, like a lathe or a router, wear a face shield to safeguard your eyes and face from flying chips and splinters.
Steel Tip Boots: In environments where you're moving heavy lumber or using large machines, steel tip boots are vital. They protect your feet from crush injuries caused by falling objects or accidentally dropping tools.
Finger Wrap Tape: In case, you’re doing detailed work with hand tools or handling materials that might slip or cause blisters, use finger wrap tape. They offer added grip and protect skin from cuts.
Storage and Organization Tools for Woodworking
Proper organization of tools not only keeps your workspace tidy but also ensures that everything has its place, which reduces clutter and saves time during project setup.
Here are storage tools to organize things:
Pegboards: A pegboard is a wall-mounted panel with holes for hooks and pegs. It is best for hanging tools in plain sight. Use it to organize hammers, screwdrivers, and wrenches. It makes them easily accessible and frees up workspace on benches and shelves.
Magnetic Strips: Magnetic strips are perfect for storing metal tools and accessories. Mount them on a wall or under a cabinet to keep items like drill bits, chisels, and knives secure yet within reach.
Storage Bins and Cabinets: Bins and cabinets are essential for categorizing and housing smaller items and bulk materials. Use storage bins to sort screws, nails, and other small hardware. Cabinets with drawers are great for organizing larger tools, safety equipment, and materials.
The Game Changer: Laser Cutting Machines
Among all the tools we have listed in the article, the most technologically advanced tools are laser cutting and engraving machines. They use a laser beam to cut and engrave wood with unparalleled precision and speed.
These machines are remarkably user-friendly, even for beginners. Just load your digital design, place your wood inside, and let the machine take over. There’s no fuss over manual adjustments.
In the cutting and engraving segment, laser machines excel without contest. They effortlessly etch detailed patterns or carve deep engravings into wood. With xTool laser cutters, safety is also front and center. Thanks to their fully enclosed design, laser filtration, and efficient exhaust systems, you’re protected as you work.
What can be made? There is a range of wood crafts you can make – from custom signboards and captivating wall art to personalized gifts and intricate jewelry.

More Woodworking Tools
We have tried to cover all the essential woodworking tools. But, there are multiple others you can use. Some additional ones include:
- Digital Caliper
- Wood Lathe
- Mortise Machine
- Featherboard
- Bench Grinder
- Wood Chisel Set
- Brad Nailer
- Bevel Gauges
- Rasps and Files
Related reading: