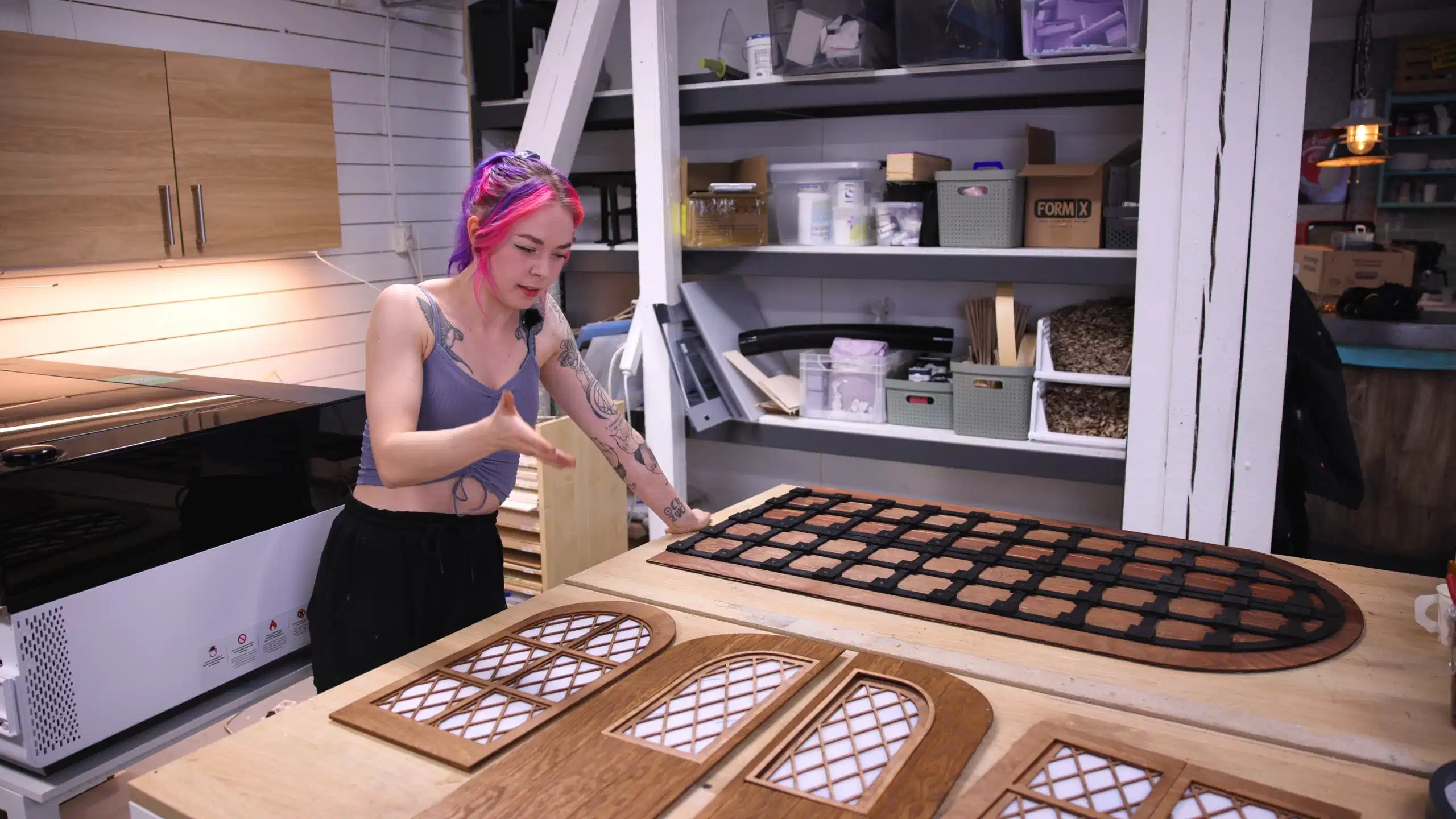
Laser cutting is highly regarded for its precision. It accurately cuts parts to match design specifications, with no room for error. One key term linked to this precision is ‘kerf’. It is responsible for keeping laser cut parts within the designated tolerance range.
Curious about this key parameter? Continue reading. This article explains the concept of kerf in laser cutting, the factors that influence it, and why kerf width is essential for precision cutting.
In This Article
- What Is Kerf in Laser Cutting?
- Factors Influencing Laser Cutting Kerf Width
- When You Need to Take Kerf into Account?
- Optimizing Kerf in Laser Cutting Processes
- Conclusion
What Is Kerf in Laser Cutting?
When a laser beam strikes a material, it vaporizes a small portion of that material to create the cut. This vaporized area leaves a gap (cut), which we call ‘kerf’. It is also termed ‘kerf width’ since it’s the width of that cut.

©Parts Fabricator
Ideally, its value should be the same as the laser spot size. However, multiple factors influence and change that. In general, the laser cutting kerf can be anywhere between 0.08mm to 1mm. That means, it can cut to up to 1mm extra along the edges of the original design.
Therefore, this value needs to be considered in the design phase. In drawings, with cutouts smaller than the kerf width, the intricacies probably get eliminated during the cutting. To avoid any surprises, factor in the kerf width when planning your design.
Factors Influencing Laser Cutting Kerf Width
Kerf Width isn’t inherently dependent on the laser machine only. Instead, it depends on a range of factors such as the material type, its thickness, the power and speed, and the type of cuts you’re making.
Laser Spot Size
Spot size is the laser beam’s diameter, so it’s the primary factor that influences laser cut kerf. The material burns according to the spot size as it is the first point of contact. Usually, kerf width is nearly equal to or slightly more than the laser spot size.
Material Thickness
The thickness of the material plays a significant role. Since the laser beam often has a slightly conical shape (see the figure), it widens as it penetrates deeper into the material. This means the kerf at the surface is smaller than at the bottom of a thick material.

Focus Position
If the laser is focused precisely on the surface, it can lead to a narrower kerf. If the focus is deeper within the material, the spot size at the surface might be larger, leading to a wider kerf.
Material Type
Materials do influence the laser kerf. Metals, due to their higher resistance to laser heat, typically have a smaller kerf (0.15mm to 0.38mm) compared to materials like wood and plastics (0.25mm to 0.51mm.). This is because they can withstand the laser's heat without substantial material loss. Wood and plastics are flammable, and burn readily, so we see slightly larger kerf widths.
Power and Cutting Speed
A research study on a CO2 laser cutting process revealed that raising the power of a laser cutter increases the kerf width. This is because higher power means more energy is concentrated on the material. Consequently, more material gets removed.

©Omer Keles, Ufuk Oner via Research Gate
However, when the cutting speed is increased along with the power, a decline in kerf width is observed. This phenomenon aligns with laser cutting principles. With a higher cutting speed, the laser beam spends less time in one spot. As a result, despite the increased power, the beam doesn’t remove as much material because it is moving faster across the surface.
Types of Cuts
The nature of the cuts – whether they are straight paths or curved lines – also impacts kerf width. Straight cuts are more uniform and can be done with consistent speed and power settings. This results in a consistent kerf width.
Curved lines require the laser to change direction and possibly speed. These variations can lead to inconsistencies in kerf width. For instance, when the laser slows down to navigate a curve, it might remove more material at the curve, which leads to a wider kerf at that point.
Although each of these factors independently influences kerf width, their effects are not isolated. The interplay between them is what determines the final kerf width in laser cutting.
When You Need to Take Kerf into Account?
In parts with simple geometry, such as industrial components, the kerf doesn’t affect the outcome. However, in designs with a lot of small geometrical features, the kerf width becomes a significant factor. Since the laser removes a certain amount of material, it can result in the loss of small details. For instance, if you need to engrave small slots within a material; it may be hard to do so if their size is less than kerf width.
Similarly, when making intricate designs, such as those required in jewelry making, kerf width dictates the sizes and intricacy of those patterns.
Optimizing Kerf in Laser Cutting Processes
Kerf is a critical parameter in laser, which needs to be seriously adjusted when cutting different objects. Here’s how it can be adjusted to optimize the cutting:
Machine Level Adjustments
You can offset the laser’s path and let it cut slightly outside the part's specified line. This offset equals the kerf width and compensates for the material it removes preserving the original design's dimensions.
Manual Design Tweaks
Designers can account for the kerf within their drawings. They do this by adding or subtracting the kerf width from their component dimensions.
Adjustments through Software
Modern laser cutter software, like Lightburn, have kerf width adjustment features. They let you set the kerf width based on material, power, and thickness. The machine automatically sets the cutting path to incorporate these settings.
Conclusion
Keeping an eye on kerf is the key to transforming good laser cutting work into great laser cutting artistry. Although its value may be insignificant in large-sized or simple crafts, it does affect the outcome for smaller intricate designs.
To keep things smooth sailing, a good rule of thumb is to make sure your cuts and the material thickness are at least as big as the laser’s kerf width.